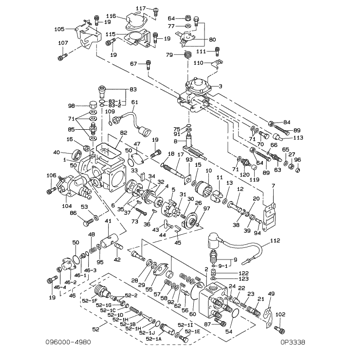
Rating:
Information washer, adjusting Denso
Include in ##:
09600-04980
as WASHER, ADJUSTING
Cross reference number
Part num
Firm num
Firm
Name
09656-90230
WASHER, ADJUSTING
Information:
Introduction
For Specifications with illustrations, make reference to Specifications for 3306 Direct Injection Vehicular Engine With New Scroll Fuel System, Form No. SENR2147. If the Specifications in Form SENR2147 are not the same as in the Systems Operation and the Testing and Adjusting, look at the printing date on the back cover of each book. Use the Specifications given in the book with the latest date.Engine Design
Cylinder And Valve LocationBore ... 120.7 mm (4.75 in)Stroke ... 152.4 mm (6.00 in)Number of Cylinders ... 6Cylinder Arrangement ... in lineValves per Cylinder ... 2Combustion ... Direct InjectionFiring Order (Injection Sequence) ... 1,5,3,6,2,4Rotation of Crankshaft (when seen from flywheel end) ... counterclockwise The No. 1 cylinder is opposite the flywheel end.Fuel System
Fuel Flow
Fuel System Schematic
(1) Fuel tank. (2) Fuel return line. (3) Priming pump. (4) Fuel injection nozzle. (5) Fuel injection line. (6) Fuel injection pump. (7) Primary fuel filter. (8) Check valves. (9) Fuel transfer pump. (10) Secondary fuel filter. (11) Constant bleed valve. (12) Fuel injection pump housing.Fuel is pulled from fuel tank (1) through primary fuel filter (7) and check valves (8) by fuel transfer pump (9). From the fuel transfer pump the fuel is pushed through secondary fuel filter (10) and to the fuel manifold in fuel injection pump housing (12). A bypass valve in the fuel transfer pump keeps the fuel pressure in the system at 25 to 40 psi (170 to 280 kPa). Constant bleed valve (11) lets a constant flow of fuel go through fuel return line (2) back to fuel tank (1). The constant bleed valve returns approximately 9 gal. (34 liters) per hour of fuel and air to the fuel tank. This helps keep the fuel cool and free of air. There is also a manual bleed valve that can be used when the fuel priming pump is used to remove air from the system. Fuel injection pump (6) gets fuel from the fuel manifold and pushes fuel at very high pressure through fuel line (5) to fuel injection nozzle (4). The fuel injection nozzle has very small holes in the tip that change the flow of fuel to a very fine spray that gives good fuel combustion in the cylinder.Fuel Injection Pump
The fuel injection pump increases the pressure of the fuel and sends an exact amount of fuel to the fuel injection nozzle. There is one fuel injection pump for each cylinder in the engine.The fuel injection pump is moved by cam (14) of the fuel pump camshaft. When the camshaft turns, the cam raises lifter (11) and pump plunger (6) to the top of the stroke. The pump plunger always makes a full stroke. As the camshaft turns farther, spring (8) returns
For Specifications with illustrations, make reference to Specifications for 3306 Direct Injection Vehicular Engine With New Scroll Fuel System, Form No. SENR2147. If the Specifications in Form SENR2147 are not the same as in the Systems Operation and the Testing and Adjusting, look at the printing date on the back cover of each book. Use the Specifications given in the book with the latest date.Engine Design
Cylinder And Valve LocationBore ... 120.7 mm (4.75 in)Stroke ... 152.4 mm (6.00 in)Number of Cylinders ... 6Cylinder Arrangement ... in lineValves per Cylinder ... 2Combustion ... Direct InjectionFiring Order (Injection Sequence) ... 1,5,3,6,2,4Rotation of Crankshaft (when seen from flywheel end) ... counterclockwise The No. 1 cylinder is opposite the flywheel end.Fuel System
Fuel Flow
Fuel System Schematic
(1) Fuel tank. (2) Fuel return line. (3) Priming pump. (4) Fuel injection nozzle. (5) Fuel injection line. (6) Fuel injection pump. (7) Primary fuel filter. (8) Check valves. (9) Fuel transfer pump. (10) Secondary fuel filter. (11) Constant bleed valve. (12) Fuel injection pump housing.Fuel is pulled from fuel tank (1) through primary fuel filter (7) and check valves (8) by fuel transfer pump (9). From the fuel transfer pump the fuel is pushed through secondary fuel filter (10) and to the fuel manifold in fuel injection pump housing (12). A bypass valve in the fuel transfer pump keeps the fuel pressure in the system at 25 to 40 psi (170 to 280 kPa). Constant bleed valve (11) lets a constant flow of fuel go through fuel return line (2) back to fuel tank (1). The constant bleed valve returns approximately 9 gal. (34 liters) per hour of fuel and air to the fuel tank. This helps keep the fuel cool and free of air. There is also a manual bleed valve that can be used when the fuel priming pump is used to remove air from the system. Fuel injection pump (6) gets fuel from the fuel manifold and pushes fuel at very high pressure through fuel line (5) to fuel injection nozzle (4). The fuel injection nozzle has very small holes in the tip that change the flow of fuel to a very fine spray that gives good fuel combustion in the cylinder.Fuel Injection Pump
The fuel injection pump increases the pressure of the fuel and sends an exact amount of fuel to the fuel injection nozzle. There is one fuel injection pump for each cylinder in the engine.The fuel injection pump is moved by cam (14) of the fuel pump camshaft. When the camshaft turns, the cam raises lifter (11) and pump plunger (6) to the top of the stroke. The pump plunger always makes a full stroke. As the camshaft turns farther, spring (8) returns