Rating:
Information pump assy, supply Denso
Compare Prices: .
As an associate, we earn commssions on qualifying purchases through the links below
Diesel Common Rail Fuel Pump 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Compatible For ISUZU Engine
TINEOOC OEM NO. 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 || Diesel Common Rail Fuel Pump 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Compatible For ISUZU Engine || ⚙️ The name of my store is: A spare parts king, here is the car parts you want! || ⚙️ The fuel pump is equipped with a standardized interface for quick and easy installation, no additional tools or modifications are required, and vehicle owners can easily replace it by themselves. || ⚙️ Optimized design and advanced technology ensure that the fuel pump provides a constant and stable fuel supply, enhancing the overall performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle.
TINEOOC OEM NO. 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 || Diesel Common Rail Fuel Pump 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Compatible For ISUZU Engine || ⚙️ The name of my store is: A spare parts king, here is the car parts you want! || ⚙️ The fuel pump is equipped with a standardized interface for quick and easy installation, no additional tools or modifications are required, and vehicle owners can easily replace it by themselves. || ⚙️ Optimized design and advanced technology ensure that the fuel pump provides a constant and stable fuel supply, enhancing the overall performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle.
Diesel Common Rail Fuel Pump 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Compatible For ISUZU Engine
TINEOOC OEM NO. 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 || Diesel Common Rail Fuel Pump 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Compatible For ISUZU Engine || ⚙️ The name of my store is: A spare parts king, here is the car parts you want! || ⚙️ The fuel pump is equipped with a standardized interface for quick and easy installation, no additional tools or modifications are required, and vehicle owners can easily replace it by themselves. || ⚙️ Optimized design and advanced technology ensure that the fuel pump provides a constant and stable fuel supply, enhancing the overall performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle.
TINEOOC OEM NO. 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 || Diesel Common Rail Fuel Pump 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Compatible For ISUZU Engine || ⚙️ The name of my store is: A spare parts king, here is the car parts you want! || ⚙️ The fuel pump is equipped with a standardized interface for quick and easy installation, no additional tools or modifications are required, and vehicle owners can easily replace it by themselves. || ⚙️ Optimized design and advanced technology ensure that the fuel pump provides a constant and stable fuel supply, enhancing the overall performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle.
MeiHongHong Compatible For ISUZU Engine 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 Replacement Fuel Pump
MeiHongHong Compatible For ISUZU Engine || 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 || Replacement Fuel Pump || fuel pump module assembly can prevent noise from the fuel tank, difficult to start, and high temperature standstill || direct replacement of OEM components, easy installation
MeiHongHong Compatible For ISUZU Engine || 294000-0490 294000-0493 8-97381555-6 || Replacement Fuel Pump || fuel pump module assembly can prevent noise from the fuel tank, difficult to start, and high temperature standstill || direct replacement of OEM components, easy installation
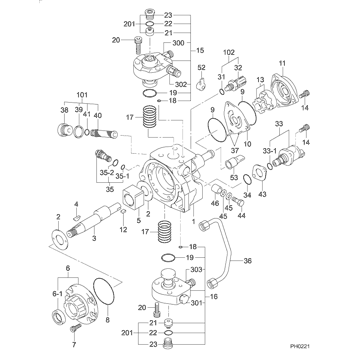
Components :
Scheme #.#:
№
Qty
Part num
Name
Remarks
Manufacture num
000
[01]
29400-00493
PUMP ASSY, SUPPLY
HP3
0711-
8-97381555-3
ISUZU
Include in ##:
29400-00493
as PUMP ASSY, SUPPLY
Cross reference number
Part num
Firm num
Firm
Name
29400-00493
8-97381555
PUMP ASSY, SUPPLY
Information:
Engine Design
CYLINDER AND VALVE LOCATIONBore ... 5.40 in.(137.2 mm)Stroke ... 6.50 in.(165.1 mm)Number and Arrangement of Cylinders ... 6, In LineFiring Order (Injection Sequence) ... 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4No. 1 Cylinder Location ... FrontRotation of Crankshaft (when seen from flywheel end) ... counterclockwiseRotation of Fuel Pump Camshaft (when seen from pump drive end) ... counterclockwiseFuel System
FUEL SYSTEM
1. Injection valve. 2. Anti-siphon block. 3. Injection pump housing. 4. Priming pump. 5. Plug. 6. Secondary filter. 7. Fuel line. 8. Return line to tank. 9. Fuel tank. 10. Primary filter. 11. Transfer pump.This engine has a pressure type fuel system. There is a single injection pump and injection valve (1) for each cylinder. The injection pumps are in the pump housing (3) on the left side of the engine. The injection valves (1) are in the precombustion chambers or adapters under the valve cover.The transfer pump (11) pulls fuel from the fuel tank (9) through the primary filter (10) and sends it through the base of priming pump (4) and the secondary filter (6), through the anti-siphon block (2) and to the manifold of the injection pump housing. When priming pump (4) is not used, the position of fuel line (7) and plug (5) are reversed. The fuel in the manifold of the injection pump housing goes to the injection pumps. The injection pumps are in time with the engine and send fuel to the injection valves under high pressure.Some of the fuel in the manifold is constantly sent back through the anti-siphon block (2) and through the return line (8) to the fuel tank to remove air from the system. Orifices in the anti-siphon block control the amount of fuel that goes back to the fuel tank.The priming pump (4) is used to remove air from the fuel filter, fuel lines and components.The transfer pump has a bypass valve and a check valve. The bypass valve (lower side) gives control to the pressure of the fuel. The extra fuel goes to the inlet of the pump.Fuel Injection Pump Operation
Injection pump plungers (4) and lifters (8) are lifted by cams on camshaft (9) and always make a full stroke. The force of springs (5) hold the lifters (8) against the cams of the camshaft.Fuel from fuel manifold (1) goes through inlet passage (2) in the barrel and then into the chamber above plunger (4). During injection, the camshaft cam moves plunger (4) up in the barrel. This movement will close inlet passage (2) and push the fuel out through the fuel lines to the injection valves.The amount of fuel sent to the injection valves is controlled by turning plunger (4) in the barrel. When the governor moves fuel rack (7), the fuel rack moves gear (6) that is fastened to the bottom of plunger (4).
CROSS SECTION OF THE HOUSING FOR THE FUEL INJECTION PUMPS
1. Fuel manifold. 2. Inlet passage in pump barrel. 3. Check valve. 4. Pump plunger. 5. Spring. 6. Gear. 7. Fuel rack. 8. Lifter. 9.
CYLINDER AND VALVE LOCATIONBore ... 5.40 in.(137.2 mm)Stroke ... 6.50 in.(165.1 mm)Number and Arrangement of Cylinders ... 6, In LineFiring Order (Injection Sequence) ... 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4No. 1 Cylinder Location ... FrontRotation of Crankshaft (when seen from flywheel end) ... counterclockwiseRotation of Fuel Pump Camshaft (when seen from pump drive end) ... counterclockwiseFuel System
FUEL SYSTEM
1. Injection valve. 2. Anti-siphon block. 3. Injection pump housing. 4. Priming pump. 5. Plug. 6. Secondary filter. 7. Fuel line. 8. Return line to tank. 9. Fuel tank. 10. Primary filter. 11. Transfer pump.This engine has a pressure type fuel system. There is a single injection pump and injection valve (1) for each cylinder. The injection pumps are in the pump housing (3) on the left side of the engine. The injection valves (1) are in the precombustion chambers or adapters under the valve cover.The transfer pump (11) pulls fuel from the fuel tank (9) through the primary filter (10) and sends it through the base of priming pump (4) and the secondary filter (6), through the anti-siphon block (2) and to the manifold of the injection pump housing. When priming pump (4) is not used, the position of fuel line (7) and plug (5) are reversed. The fuel in the manifold of the injection pump housing goes to the injection pumps. The injection pumps are in time with the engine and send fuel to the injection valves under high pressure.Some of the fuel in the manifold is constantly sent back through the anti-siphon block (2) and through the return line (8) to the fuel tank to remove air from the system. Orifices in the anti-siphon block control the amount of fuel that goes back to the fuel tank.The priming pump (4) is used to remove air from the fuel filter, fuel lines and components.The transfer pump has a bypass valve and a check valve. The bypass valve (lower side) gives control to the pressure of the fuel. The extra fuel goes to the inlet of the pump.Fuel Injection Pump Operation
Injection pump plungers (4) and lifters (8) are lifted by cams on camshaft (9) and always make a full stroke. The force of springs (5) hold the lifters (8) against the cams of the camshaft.Fuel from fuel manifold (1) goes through inlet passage (2) in the barrel and then into the chamber above plunger (4). During injection, the camshaft cam moves plunger (4) up in the barrel. This movement will close inlet passage (2) and push the fuel out through the fuel lines to the injection valves.The amount of fuel sent to the injection valves is controlled by turning plunger (4) in the barrel. When the governor moves fuel rack (7), the fuel rack moves gear (6) that is fastened to the bottom of plunger (4).
CROSS SECTION OF THE HOUSING FOR THE FUEL INJECTION PUMPS
1. Fuel manifold. 2. Inlet passage in pump barrel. 3. Check valve. 4. Pump plunger. 5. Spring. 6. Gear. 7. Fuel rack. 8. Lifter. 9.