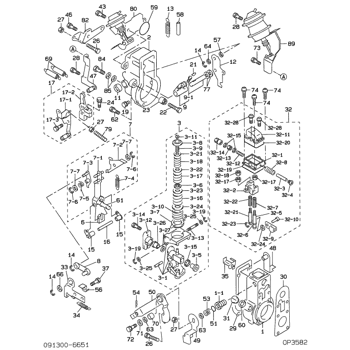
Rating:
Information lever sub-assy, st Denso
Include in ##:
09130-06653
as LEVER SUB-ASSY, ST
Cross reference number
Part num
Firm num
Firm
Name
09109-01690
22348-4660
LEVER SUB-ASSY, ST
0910901690
22348-4660A
HINO
LEVER SUB-ASSY, ST
0910901690
S2234-84660-A
HINO
LEVER SUB-ASSY, ST
Information:
Every 80,000 gal (303 200 L) of Fuel or 500,000 Miles (805 000 km) or 10,000 Hours
The overhaul column in the Maintenance Management Schedule gives Caterpillar's recommendation for performing an overhaul. The interval is expressed in total amount of fuel consumed as well as odometer distance and service hours, whichever occurs first. The best figure to use is total fuel consumed, even if this figure is estimated. Fuel consumption more closely follows the load upon the engine.The hours figure is an average value for a reasonable load factor. The hours figure will be too high if the engine is run at high load and too low if the engine is lightly loaded.Use the fuel consumption, odometer distance or service hour figure only as a guideline. Other factors, such as how conscientiously preventive maintenance has been performed, fuel quality, operating conditions, S O S results, etc., are important in deciding when to perform an overhaul, as well as some important economic points to keep in mind. You must read and understand the warnings and instructions contained in the Safety section of this manual before performing any operation or maintenance procedures.According to the Maintenance Management Schedule, it's time to have the engine overhauled. However, with the exception of burning a little oil and experiencing a slight increase in fuel consumption, there are not any other problems with the truck engine.The choice to continue running or to overhaul the engine is the owner operators responsibility. However, failures are almost inevitable. Maybe there won't be a failure in the immediate future, but there will be a failure at some point in time. The figures shown in the following scenario are based on certain assumptions for the purpose of presenting an example only.The truck has 525,000 miles (845 250 km) on its 3176 Engine. If the truck runs for 75,000 more miles (120 750 km) and then fails, the repair cost will be between U.S. $.0085 and U.S. $.0153 cents per mile (km). However, if you choose to repair your engine before it fails, by performing an in-frame overhaul at a cost of U.S. $3700, the repair cost will only be U.S. $.007 cents per mile (km). The difference between the repair before failure cost and the after failure cost is the result of damage to other engine parts when a major failure occurs. This is money that is not only wasted, but is money that could have been used more profitably elsewhere.By not performing an overhaul, the risk of seizing a piston, breaking a rod, fatiguing a bearing or causing other severe damage to the engine. The cost to repair this damage could range from U.S. $5000 to $9000 and the amount of downtime encountered would exceed the amount of downtime required for a scheduled in-frame overhaul.Consider the alternatives: Spend U.S. $3700 to overhaul your engine, with minimal downtime, before failure or spend U.S. $5000 to $9000 in repairs, with several days of unscheduled downtime, after the engine fails.It is evident by
The overhaul column in the Maintenance Management Schedule gives Caterpillar's recommendation for performing an overhaul. The interval is expressed in total amount of fuel consumed as well as odometer distance and service hours, whichever occurs first. The best figure to use is total fuel consumed, even if this figure is estimated. Fuel consumption more closely follows the load upon the engine.The hours figure is an average value for a reasonable load factor. The hours figure will be too high if the engine is run at high load and too low if the engine is lightly loaded.Use the fuel consumption, odometer distance or service hour figure only as a guideline. Other factors, such as how conscientiously preventive maintenance has been performed, fuel quality, operating conditions, S O S results, etc., are important in deciding when to perform an overhaul, as well as some important economic points to keep in mind. You must read and understand the warnings and instructions contained in the Safety section of this manual before performing any operation or maintenance procedures.According to the Maintenance Management Schedule, it's time to have the engine overhauled. However, with the exception of burning a little oil and experiencing a slight increase in fuel consumption, there are not any other problems with the truck engine.The choice to continue running or to overhaul the engine is the owner operators responsibility. However, failures are almost inevitable. Maybe there won't be a failure in the immediate future, but there will be a failure at some point in time. The figures shown in the following scenario are based on certain assumptions for the purpose of presenting an example only.The truck has 525,000 miles (845 250 km) on its 3176 Engine. If the truck runs for 75,000 more miles (120 750 km) and then fails, the repair cost will be between U.S. $.0085 and U.S. $.0153 cents per mile (km). However, if you choose to repair your engine before it fails, by performing an in-frame overhaul at a cost of U.S. $3700, the repair cost will only be U.S. $.007 cents per mile (km). The difference between the repair before failure cost and the after failure cost is the result of damage to other engine parts when a major failure occurs. This is money that is not only wasted, but is money that could have been used more profitably elsewhere.By not performing an overhaul, the risk of seizing a piston, breaking a rod, fatiguing a bearing or causing other severe damage to the engine. The cost to repair this damage could range from U.S. $5000 to $9000 and the amount of downtime encountered would exceed the amount of downtime required for a scheduled in-frame overhaul.Consider the alternatives: Spend U.S. $3700 to overhaul your engine, with minimal downtime, before failure or spend U.S. $5000 to $9000 in repairs, with several days of unscheduled downtime, after the engine fails.It is evident by